Please notice all information provided by Qbridge is just for reference, the copyright and any other right of and in relation to which is solely owned by Qbridge or any other party it designates to. It is not allowed to use such information for profit, otherwise Qbridge reserves the right to pursue your liabilities.
by Big Data DT
Apply for 30 mins FREE Consulting!
There are various kinds of data within an enterprise, including:
- Business data of enterprises, such as financial statements, cash flow, daily number of activators and active number of products;
- Data required for enterprise decision-making, such as industry statistical reports; All kinds of data collected by products, including user registration information and behavior information;
- Data processed and developed by enterprises on the basis of various types of data collected, such as user portraits, recommended algorithm models, product optimization directions, etc.
Data compliance governs user related data, the specific boundaries are not clear, and the terms are different. Some call it user data, some call it personal information, and most call it privacy.
What is the scope of data compliance work? From the nature of information technology, personal information is one or more fields, that is, data. For example, “01010202, F, click, 2021-04-21 9:26:00”, the data in this row is based on the customized data structure, which means “ID is 01010202, gender is female, and a click occurred at 9:26 on April 21, 2021”. Data has its own life cycle, as shown in the following figure, which can be logically simply divided into data collection, use, storage, disclosure and destruction.
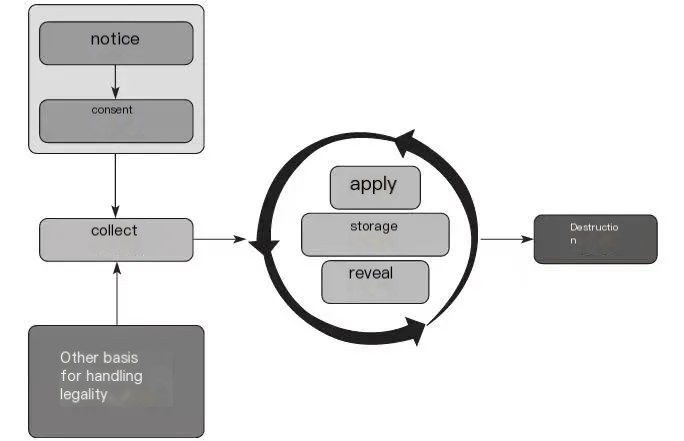
▲ Figure 1 Data Life cycle
The use of the “full life cycle of data” framework, on the one hand, conforms to the basic laws of data, and on the other hand, can help data compliance personnel comprehensively sort out the activities of enterprises in processing personal information, and then assess and dispose of the corresponding personal information protection risks in stages.
01 All Aspects of Data Compliance
- Management System
The provisions of the law on the processing of personal information by enterprises provide corresponding, appropriate and necessary organizational and technical measures for enterprises according to the risks of the activities handled. Organizational measures need to rely on the management system to operate, as shown in Figure 2, which simply includes institutional organizational guarantee of personal information protection, training and assessment of relevant employees, as well as corresponding institutional guarantee (implementation of compliance requirements into regulatory documents at different levels within the company), emergency response to security incidents and security audit.
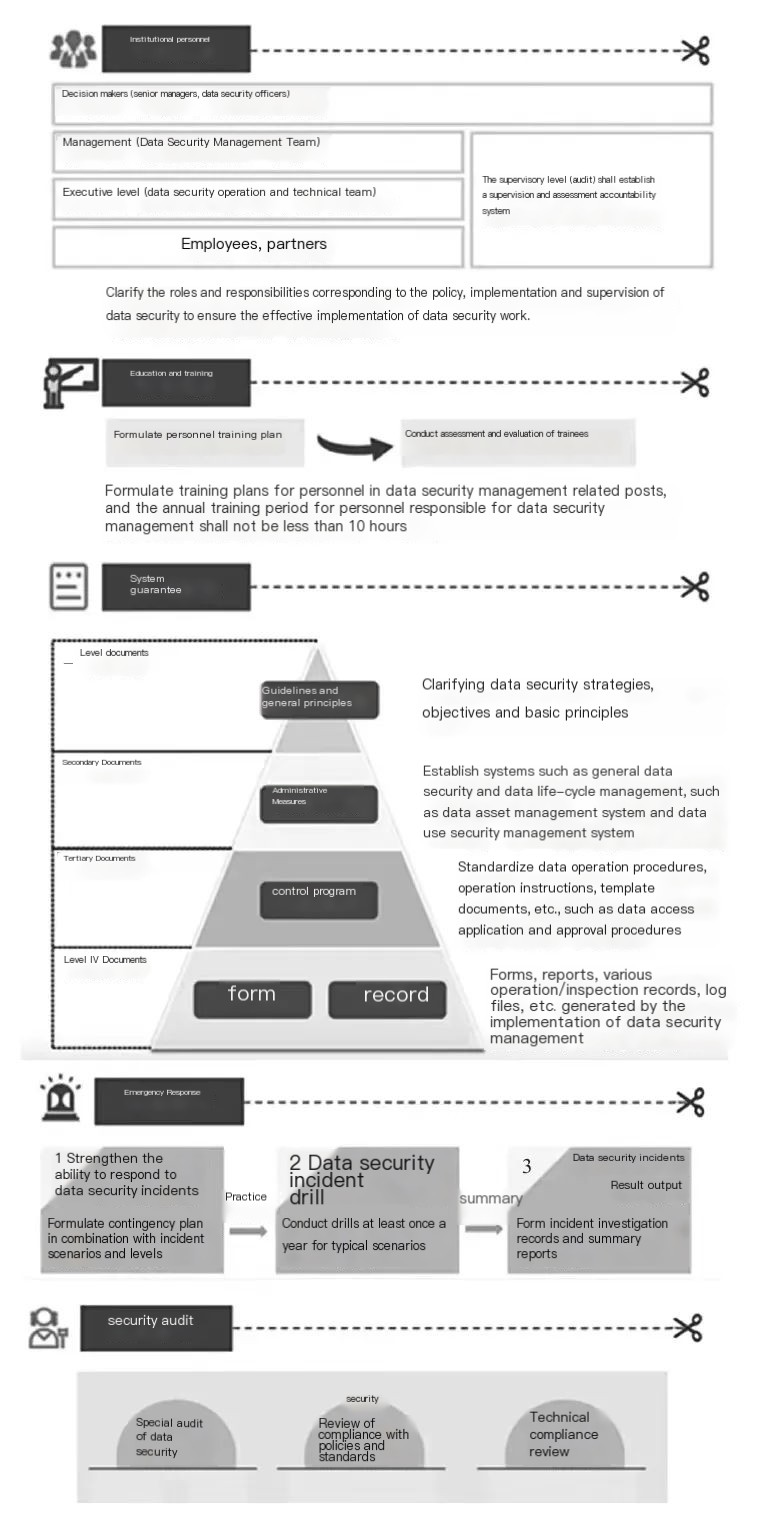
▲ Figure 2 Schematic Diagram of Personal Information Protection Management System
- Technical Measures
Appropriate and necessary measures shall include corresponding technical measures in addition to organizational measures. The scope of technical measures for personal information protection is relatively wide, including security technical measures such as encryption and desensitization, as well as product design technical measures to implement personal information protection requirements. Security technical measures, as shown in Figure 3, include data identification, personal information protection, interface security management, data leakage prevention and operational audit.
For the technical measures for product design to implement the requirements for personal information protection, the compliance control measures designed based on the risks brought by the products themselves according to the differences of various product types include differential privacy and federal computing. For example, the reading platform proposes to open the friendship relationship, and can share the reading records and experience with each other. However, this function is beyond the expectation of some users who want to read privately, so the product compliance design should not be turned on by default.
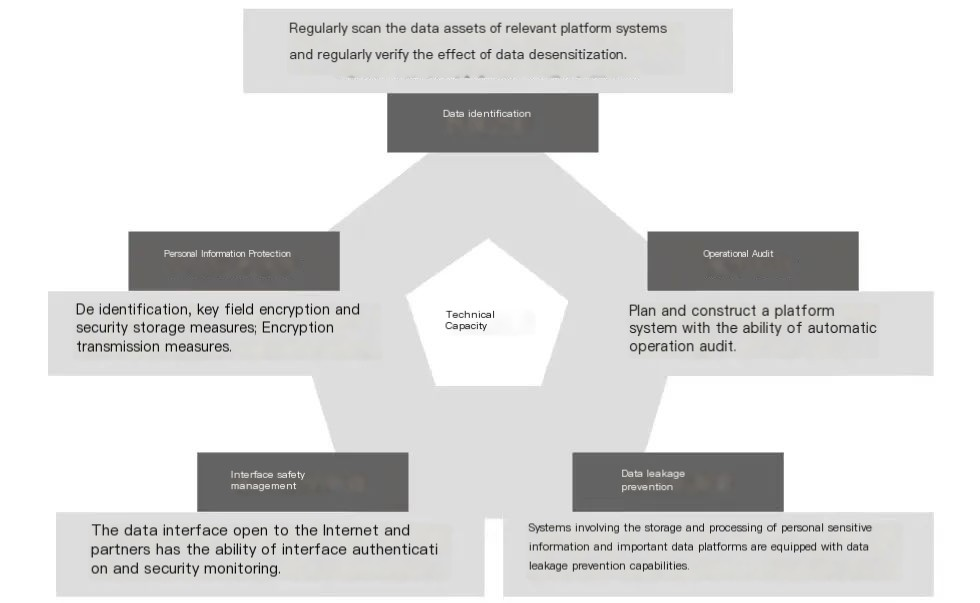
▲ Figure 3 Schematic Diagram of Technical Measures for Personal Information Protection
As mentioned above, data compliance work involves many aspects, including policy research, compliance assessment, management system and technical measures, which should be undertaken by their respective relevant departments when the division of labor within the enterprise is clear.
02 Stakeholders in Data Compliance Work
- Stakeholders Related to Functional Development
Taking software development as an example to illustrate stakeholders, as shown in Figure 4, the stakeholders involved in data compliance are as follows.
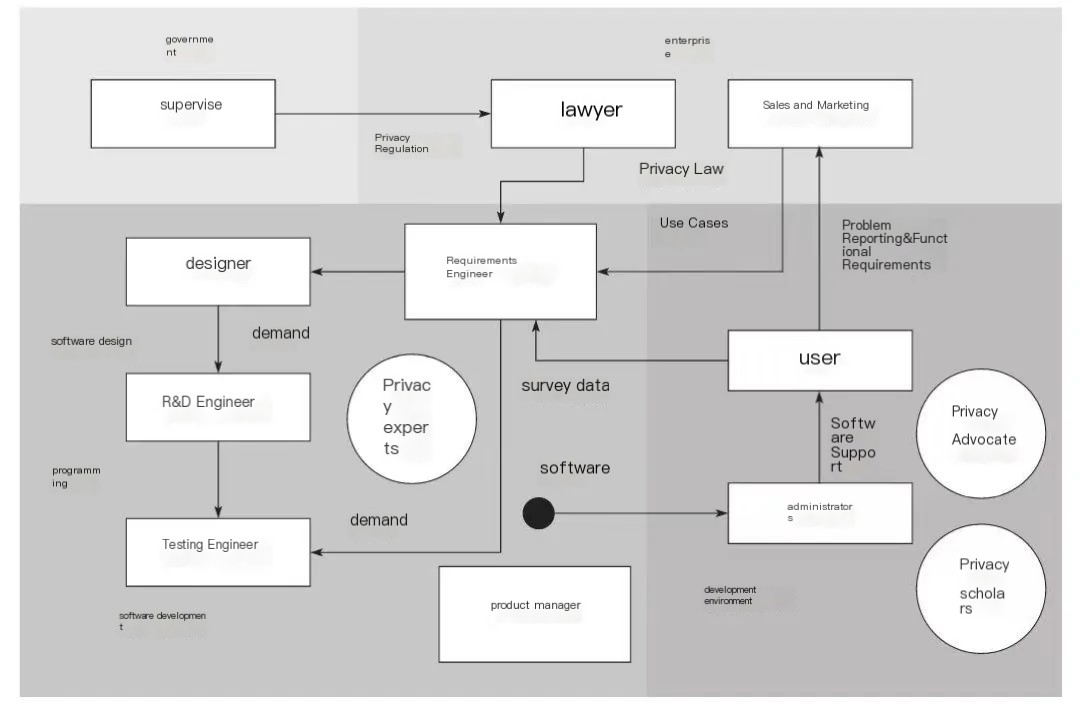
▲ Figure 4 Schematic diagram of stakeholders in personal information protection in software function development
- Relevant Stakeholders of Data Development
In the age of big data, in addition to traditional software development, more is involved in data utilization, including data analysis, data mining, in-depth learning, algorithm recommendation, user profiles, etc. There are two types of stakeholders involved in data development.
1) The data scientist department, including algorithm engineers and data engineers, is mainly responsible for realizing the needs of the business through data. For example, in online car booking services, an algorithm model is built to match users and drivers, complete the most efficient dispatch, and reduce user waiting time. To fulfill such a demand, it is necessary to analyze the data including personal information in a wide range, including the location, time and habits of centralized taxi taking by users, and build corresponding algorithm models.
The data scientist department will have a stronger demand for data than the software development related department, but for reasons such as in-depth learning, it is difficult to explain the relationship between personal information and achieving the purpose. Therefore, data compliance personnel need to work closely with data scientists to promote the value of data while safeguarding personal information protection.
2) The main responsibility of the big data platform department is to build a big data platform, including data storage architecture, metadata, data analysis engine and other infrastructure technology architecture. Big data platforms can implement personal information protection requirements on the data platform side, such as data discovery and data flow maps, provide basic materials for evaluation of personal information protection, and observe the implementation effect of compliance.
- Stakeholders of Management System and Technical Measures
As mentioned earlier, we need to establish management systems and security technical measures to safeguard personal information. Departments such as information security management systems and security attack and defense have matured before the advent of personal information protection, often referred to as the Information Security Department.
The data compliance work shall fully cooperate with the Information Security Department, increase personal information protection on the information security management system, iterate into the personal information security management system, and continuously implement and consolidate security technical measures, including vulnerability management and data leakage prevention.
Get more information tailored to your needs by click Here.

